| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
File:|dry the color film | File:|dry the color film | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
===5. References=== | ===5. References=== | ||
[1] Robert Boyle. 1664. Experiments and Considerations Touching Colours. Project Gutenberg. 1–157 pages. | # [1] Robert Boyle. 1664. Experiments and Considerations Touching Colours. Project Gutenberg. 1–157 pages. | ||
[2] Jian He and M Monica Giusti. 2010. Anthocyanins: Natural Colorants with Health-Promoting Properties | # [2] Jian He and M Monica Giusti. 2010. Anthocyanins: Natural Colorants with Health-Promoting Properties. | ||
# [3] Xiahong Zhang, Sisi Lu, and Xi Chen. 2014. A visual pH sensing film using natural dyes from Bauhinia blakeana Dunn. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 198 (2014), 268–273. | |||
# [4] Viirj Kan. 2017. Organic Primitives: Synthesis and Design of pH-Reactive Materials using Molecular I/O for Sensing, Actuation, and Interaction. Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems Pages 989-1000. | |||
# [5] UMass Amherst Department of Chemistry Lecture Demonstrations. | |||
[[:File:12.6 bio-lab first idea.pdf]] | [[:File:12.6 bio-lab first idea.pdf]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
* https://ellieirons.com/projects/two-meadows/ | * https://ellieirons.com/projects/two-meadows/ | ||
Revision as of 12:24, 31 March 2018
Object is talking
1. Introduction
1.1 anthocyanin
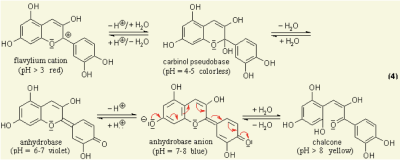
Anthocyanins are water-soluble vacuolar pigments. In the 1664 book Experiments and Considerations Touching Colours by chemist Robert Boyle, various edible plants are reported as visual pH indicators due to pH-responsive mechanisms in their tissues [1]. Anthocyanin is a kind of natural colorant in food and beverage industry, and has been found to possess anti-inflammatory antioxidant properties [2]. It has also been researched for use as an indicator for packaging applications to detect spoilage in pork and fish products [3]. All tissues of vascular plants contain the flavonoid anthocyanin, a pigment that changes colour under varying pH solutions. Under different pH conditions, the hydroxyl (OH) and/or methyl ether (O-CH3) groups attached to the carbon rings (figure 1) undergo reversible structural transformations and ionizations. Restructuring a molecule changes the way it ab- sorbs light, giving rise to colour changes [4].
Figure 1 Chemical diagram of colour-changing anthocyanin pH reaction [5]
1.2 red cabbage
"Red cabbage is rich in a number of bioactive substances, including anthocycanins"[Wiczkowski, 2012]. The method of extracting anthocyanin from red cabbage is easy and convenient.
2. Idea
This work is based on a research done by MIT media lab that uses organic fluid-based molecules. The molecules anthocyanin, vanillin, chitosan are used as dopants that can sense different pH values. The output is in the form of a broad spectrum of colors, odors and shapes. Based on this, the experiment focus on color changing, using kappa-carrageenan as substrate to present the reaction in a certain form. The outcome shows chemical reactions that are in daily life unreadable and unseen. What is shown here is a new design language to create new appliances. In the exhibition, color changing can be seen both in liquid and solid statues.
3. Methodology
- Color Changing in liquid status
- Color Changing in solid status
- Shape Changing
5. References
- [1] Robert Boyle. 1664. Experiments and Considerations Touching Colours. Project Gutenberg. 1–157 pages.
- [2] Jian He and M Monica Giusti. 2010. Anthocyanins: Natural Colorants with Health-Promoting Properties.
- [3] Xiahong Zhang, Sisi Lu, and Xi Chen. 2014. A visual pH sensing film using natural dyes from Bauhinia blakeana Dunn. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 198 (2014), 268–273.
- [4] Viirj Kan. 2017. Organic Primitives: Synthesis and Design of pH-Reactive Materials using Molecular I/O for Sensing, Actuation, and Interaction. Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems Pages 989-1000.
- [5] UMass Amherst Department of Chemistry Lecture Demonstrations.