m (Miga moved page GMU:BioArt/Iremnur Tokac to GMU:BioArt WS15/Iremnur Tokac) |
|||
| (63 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= | = Crystallization Morphology affected by Space= | ||
==The Concept== | |||
This project is an attempt to explore the crystallization process of MgSO4 and discuss whether it is affected by physical environment or not in terms of 3D geometries. The main concern of the project is to examine ways to manipulate the structure of output pattern of crystallization. Previous studies hinted that crystallization morphology differs based on the distinct height of the solution in identical containers. Therefore, the idea of testing different geometrical shapes as containers and observing the variety of crystallization outcomes as a project was occurred. The overall concept is to analyze complex structures like crystals by intervening the formalization process and evaluate the outcomes in comparison. After several experiments, we might able to unveil some computational system behind the crystal growth morphology. | |||
=First Experiments | ==First Experiments== | ||
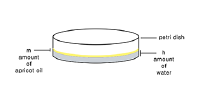
[[File:BioArt-1-petri-dish.png|200px]] | |||
:an illustration of the experiment medium | |||
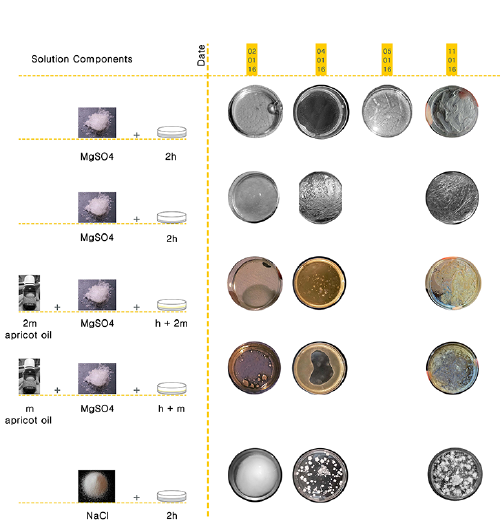
</ | ===The chart of first experiments=== | ||
[[File:BioArt-2-Chart.png|500px]] | |||
Solutions with different type and amount of components were experimented and distinct crystallization morphologies were observed. According to the results, crystallization morphology was affected by the height of the solution, which contains water and MgSO4, in identical petri dishes. If ”h” increases, the bigger, rectangular prism shaped crystals appear. On the other hand, if “h” decreases, relatively a thin and linear crystal network occurs. | |||
==Preperation For Further Experiments== | |||
===Working environment=== | |||
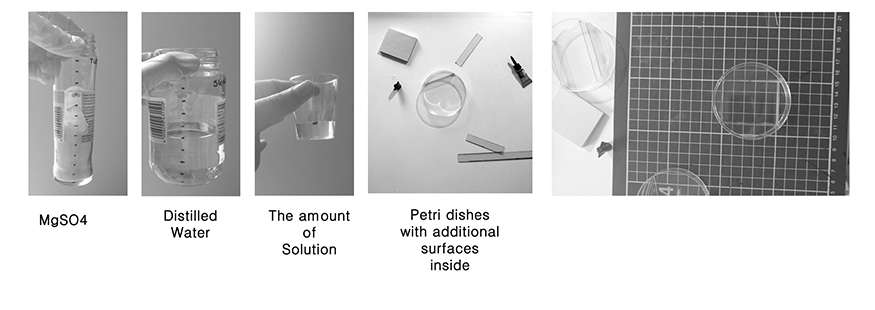
Same amount of MgSO4 and water was measured and used in every experiment. Therefore, it is assumed that the different crystallization patterns would formed based on different shapes of containers. However, it should be noted that those experiments were not held in a very well controlled LAB environment, so the results might have been affected by other unknown factors as well. | |||
[[File:BioArt-3-salt-measurement-2.png]] | |||
===Preparing Petri Dishes| Additional Surface in Petri Dishes=== | |||
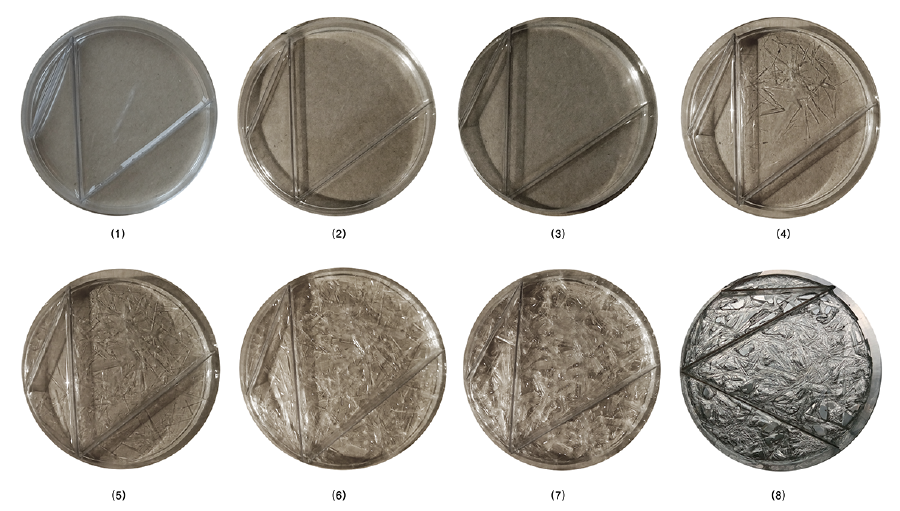
Further experiments were set up in order to explore morphological differences in crystallization regarding container shape. Therefore, transparent films were placed in petri dishes to create edges with different angles. | |||
[[File:BioArt-3-petri-dishes-exp-1.png|900px]] | |||
== Experiment Series == | |||
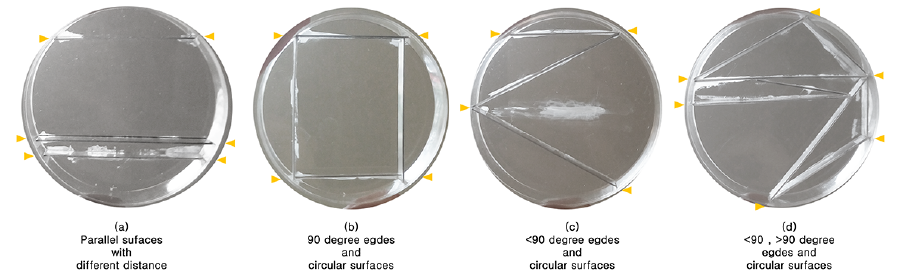
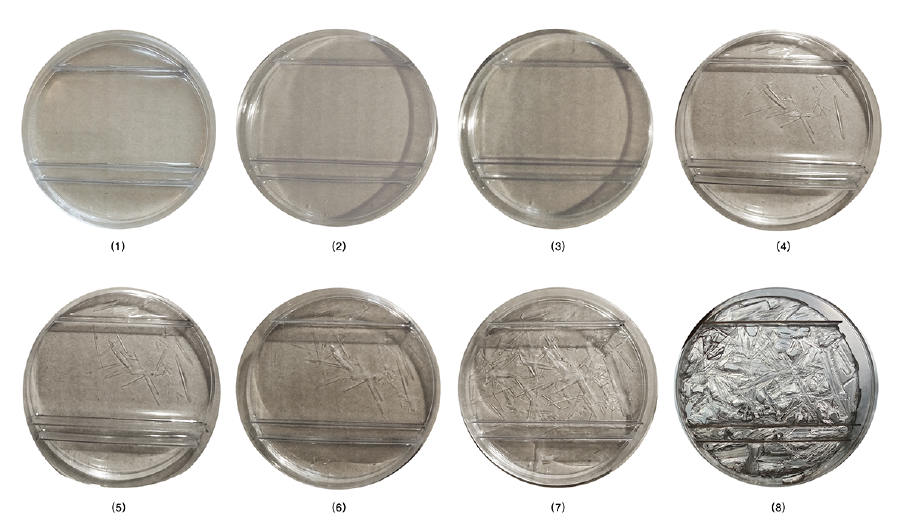
===Parallel surfaces with different distance=== | |||
[[File:BioArt-3-petri-dishes-exp-2.png|900px]] | |||
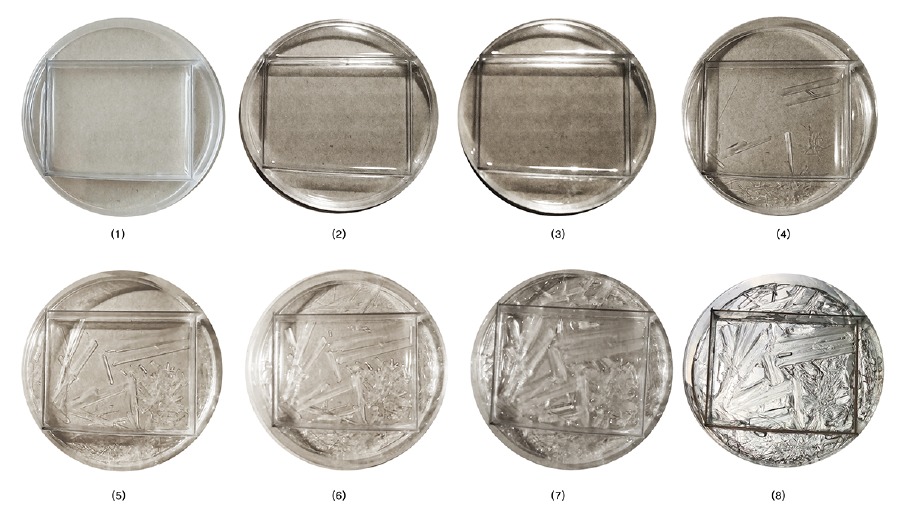
===90 degree edges and circular surfaces=== | |||
[[File:BioArt-3-petri-dishes-exp-3.png|900px]] | |||
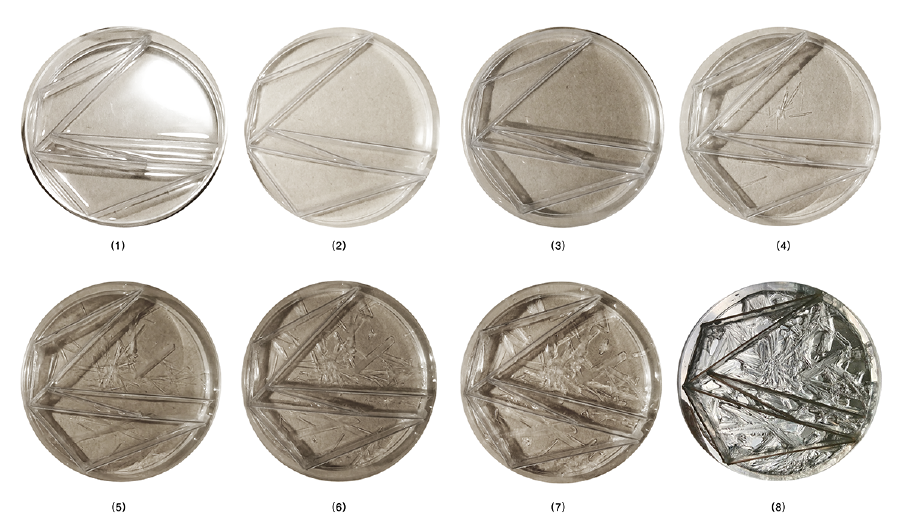
===<90 degree edges and circular surfaces=== | |||
[[File:BioArt-3-petri-dishes-exp-4.png|900px]] | |||
=== <90 degree, >90 degree edges and circular surfaces=== | |||
[[File:BioArt-3-petri-dishes-exp-5.png|900px]] | |||
[http://www.slideshare.net/iremnurtokac/crystallization-morphology] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:55, 10 October 2017
Crystallization Morphology affected by Space
The Concept
This project is an attempt to explore the crystallization process of MgSO4 and discuss whether it is affected by physical environment or not in terms of 3D geometries. The main concern of the project is to examine ways to manipulate the structure of output pattern of crystallization. Previous studies hinted that crystallization morphology differs based on the distinct height of the solution in identical containers. Therefore, the idea of testing different geometrical shapes as containers and observing the variety of crystallization outcomes as a project was occurred. The overall concept is to analyze complex structures like crystals by intervening the formalization process and evaluate the outcomes in comparison. After several experiments, we might able to unveil some computational system behind the crystal growth morphology.
First Experiments
- an illustration of the experiment medium
The chart of first experiments
Solutions with different type and amount of components were experimented and distinct crystallization morphologies were observed. According to the results, crystallization morphology was affected by the height of the solution, which contains water and MgSO4, in identical petri dishes. If ”h” increases, the bigger, rectangular prism shaped crystals appear. On the other hand, if “h” decreases, relatively a thin and linear crystal network occurs.
Preperation For Further Experiments
Working environment
Same amount of MgSO4 and water was measured and used in every experiment. Therefore, it is assumed that the different crystallization patterns would formed based on different shapes of containers. However, it should be noted that those experiments were not held in a very well controlled LAB environment, so the results might have been affected by other unknown factors as well.
Preparing Petri Dishes| Additional Surface in Petri Dishes
Further experiments were set up in order to explore morphological differences in crystallization regarding container shape. Therefore, transparent films were placed in petri dishes to create edges with different angles.
Experiment Series
Parallel surfaces with different distance
90 degree edges and circular surfaces
<90 degree edges and circular surfaces
<90 degree, >90 degree edges and circular surfaces