|
|
| Line 23: |
Line 23: |
|
| |
|
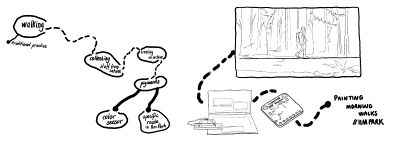
| An Arduino with a color sensor records the data and this data (variety of pigments) will be use for to paint morning walks at Ilm Park. A color will be archived while walking every morning on the specific route determined in the park. | | An Arduino with a color sensor records the data and this data (variety of pigments) will be use for to paint morning walks at Ilm Park. A color will be archived while walking every morning on the specific route determined in the park. |
|
| |
|
| |
| Code:
| |
|
| |
| import processing.serial.*; // import Serial library
| |
| Serial myPort; // Create object from Serial class
| |
| String incomingData = null; // create String "text" variable for incoming arduino data
| |
| float rawSensorData = 0; // create float "number" variable for incoming arduino data
| |
| float r,g,b;
| |
| void setup() {
| |
| size(800, 800); // define the size of the canvas
| |
| String portName = Serial.list()[3]; // define the serial port. change the number in [] to a 1 or 2 etc. to match your Arduino USB port.
| |
| myPort = new Serial(this, portName, 9600); // create new serial object with baud rate (USB-speed) 9600 (must be the same in arduino!!!)
| |
| myPort.bufferUntil('\n'); // receive data until new line character comes up
| |
| background (255); // make a white background. You can also put this in DRAW to refresh your canvas every draw loop.
| |
| }
| |
| void draw() {
| |
| //*** experiment here to visualize your sensor data!
| |
| //*** use the variable – rawSensorData – to change things according to sensor changes.
| |
| // for example:
| |
| //float mappedData = map (rawSensorData, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
| |
| background (r,g,b);
| |
| }
| |
| // this is the serial function that runs constantly in the background of your program
| |
| // it allows you to use the incoming data in the draw() function, you do not need to change this.
| |
| void serialEvent(Serial myPort) {
| |
| incomingData = myPort.readString(); // read the incoming data as String and save it in the "incomingData" variable
| |
| r = float(trim(incomingData.split(" ")[0]));
| |
| g = float(trim(incomingData.split(" ")[1]));
| |
| b = float(trim(incomingData.split(" ")[2]));
| |
| //rawSensorData = float(trim(incomingData)); // clean the incoming data String and convert it to a float data type (a number)
| |
| //println (rawSensorData); // print the data to the console for inspection
| |
| println (incomingData);
| |
| myPort.clear(); // clear the serial port for receiving new data
| |
| }
| |
| /*
| |
| HELP: FINDING THE CORRECT USB PORT
| |
| if you can not find your arduino USB port, make a new file and add this code:
| |
| * CODE START *
| |
| import processing.serial.*;
| |
| // List all the available serial ports
| |
| printArray(Serial.list());
| |
| * CODE END *
| |
| It will print out a list of all your USB connections.
| |
| Find the [ ] number for your Arduino Port and include it in line 8 of this code.
| |
| */
| |