Lea.maravic (talk | contribs) (new change) |
Lea.maravic (talk | contribs) (new photo) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
[[File:20230428 134426.jpg|thumb|1082x1082px|Preparing samples]] | [[File:20230428 134426.jpg|thumb|1082x1082px|Preparing samples]] | ||
After the preparation was finished, we loaded these samples in one neat row on a gel bed connected to electrodes. After half an hour the florescent light showed that she samples assembled themselves in columns at various lengths. We used the raspberry as our control and the raspberry sample columns all assembled themselves to the same hight as the control. We could determine which samples are of plant and which of animal origin. Very few samples were successfully put through this PCR test. | After the preparation was finished, we loaded these samples in one neat row on a gel bed connected to electrodes. After half an hour the florescent light showed that she samples assembled themselves in columns at various lengths. We used the raspberry as our control and the raspberry sample columns all assembled themselves to the same hight as the control. We could determine which samples are of plant and which of animal origin. Very few samples were successfully put through this PCR test. | ||
[[File:20230428 134817.jpg|thumb|1082x1082px|Preparing samples 2]] | [[File:20230428 134817.jpg|thumb|1082x1082px|Preparing samples 2[[File:Results.jpg|thumb|1548x1548px|Results]]]] | ||
Revision as of 18:34, 21 July 2023
WORKSHOP I
12.04.2023, 13.04.2023 - /Growing, Shaping and Living (with) Microalgae with biologist Johann Bauerfeind
WORKSHOP II.
28.04.2023, 29.04.2023 - /DNA analysis with molecular biologist Julian Chollet
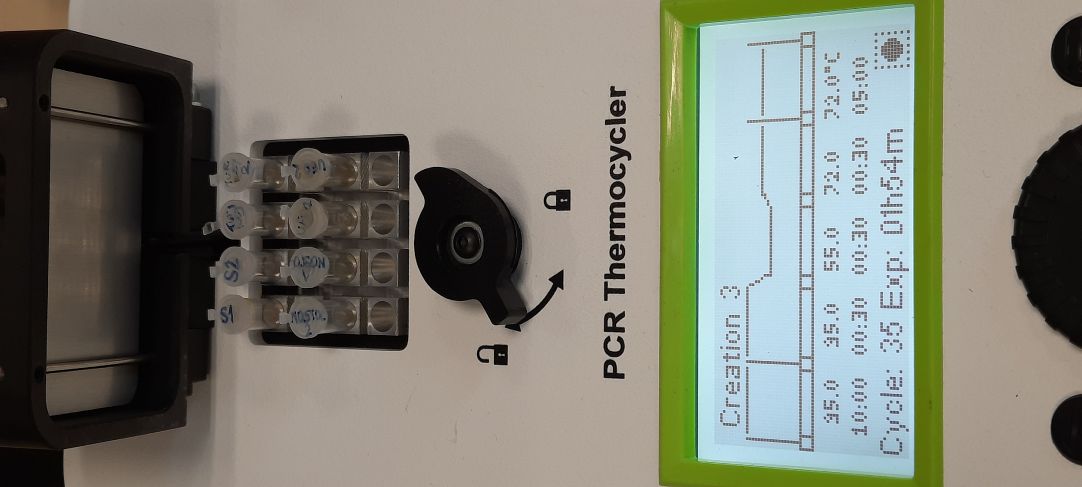
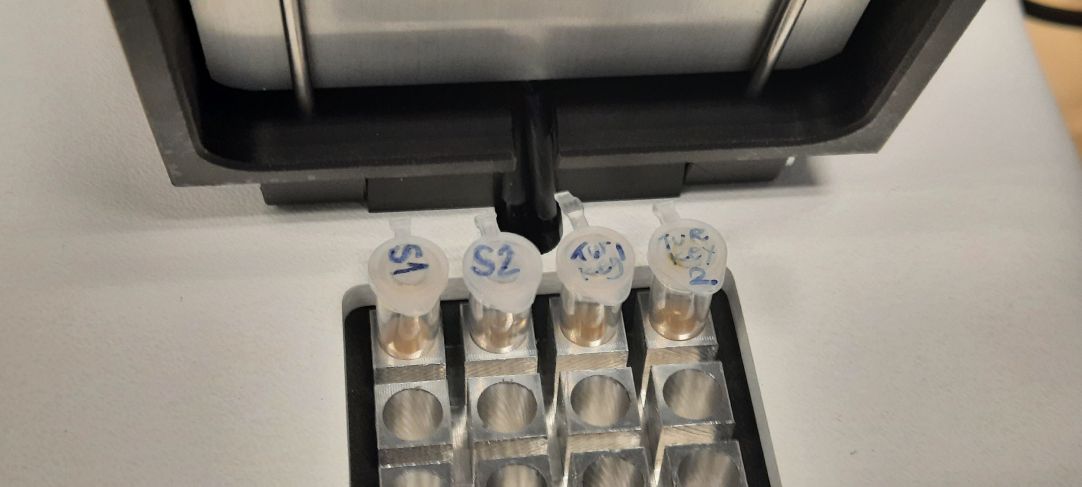
Julian is a molecular biologist who showed us how to use a diagnostic tool called PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) for DNA analysis. All living beings contain a complex molecule called DNA polymerase. It copies DNA so all organisms that want to replicate have it. In order to replicate and or analyse a DNA in a laboratory we need 3 substances: DNA or an organism we want to analyse, DNA polymerase and primers. Primers are small pieces of DNA made up in a laboratory and they can have any sequence of nucleotides.
For the experiment all the participants chose a substance to analyse and then we prepared the specimens. Mostly we worked with fruit. Some of us chose saliva as our specimen. Most specimens were prepared by first chopping, blending, mushing and centrifuging them. Then we put them through 3 stages:
1) DENATURATION - heating to 95°C to break up the connections between DNA helyx
2) ANNEALING - at the temperature of 55°C primers will attach to the basis of DNA
3) EXTENSION - the temperature of 72°C is the point when DNA polymerase replicates DNA by extending the primer. It assembles 1000 pieces of DNA at this temperature
After the preparation was finished, we loaded these samples in one neat row on a gel bed connected to electrodes. After half an hour the florescent light showed that she samples assembled themselves in columns at various lengths. We used the raspberry as our control and the raspberry sample columns all assembled themselves to the same hight as the control. We could determine which samples are of plant and which of animal origin. Very few samples were successfully put through this PCR test.