| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
Eaters are “Still Lives” which can eat away many objects without sustaining permanent damage. The job of the eater here is to assimilate the LWSSs coming in from the right. Since we have two distinct phases of LWSSs, the eater must be oriented properly to perform its job, otherwise the LWSSs will permanently destroy the eater. Kok's Galaxy belongs to the class of oscillators. Functionally, the generations of Kok's Galaxy flanking the eaters don't serve any purpose since deleting them doesn't affect the ticker at all. | Eaters are “Still Lives” which can eat away many objects without sustaining permanent damage. The job of the eater here is to assimilate the LWSSs coming in from the right. Since we have two distinct phases of LWSSs, the eater must be oriented properly to perform its job, otherwise the LWSSs will permanently destroy the eater. Kok's Galaxy belongs to the class of oscillators. Functionally, the generations of Kok's Galaxy flanking the eaters don't serve any purpose since deleting them doesn't affect the ticker at all. | ||
[[File:Memory | [[File:Memory Loop2.png|900px|left|thumb|Memory Loop]] | ||
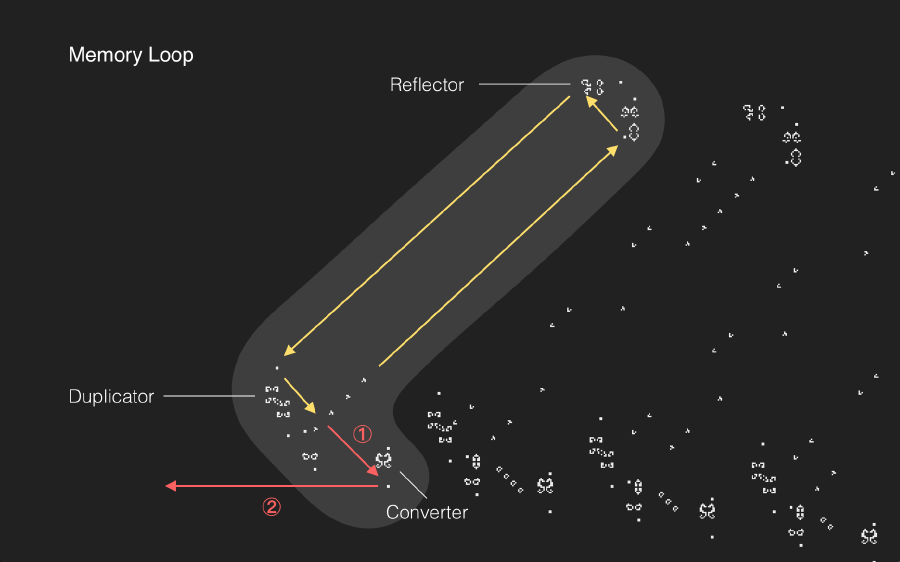
The text is generated row by row. It starts by first creating the rows in the middle — the sixth and seventh rows. Rows 1 to 6 are created by the six structures at the right-top which are called “memory loops”. The other five are created by the five memory loops at the right bottom. The memory loops hold a specific pattern made of gliders that keep looping in the structure. At one end, they are duplicated where one glider is fed to the "Converter" and the other back into the memory loop. | The text is generated row by row. It starts by first creating the rows in the middle — the sixth and seventh rows. Rows 1 to 6 are created by the six structures at the right-top which are called “memory loops”. The other five are created by the five memory loops at the right bottom. The memory loops hold a specific pattern made of gliders that keep looping in the structure. At one end, they are duplicated where one glider is fed to the "Converter" and the other back into the memory loop. | ||
The gliders loop following the yellow arrows with the help of “Reflectors” placed at either ends. Additionally at the bottom end there is a glider duplicator. It produces a glider that moves parallel to the original. While the duplicated glider is sent back into the loop, the original glider is sent to a “Converter” which converts the glider to a LWSS (moves along the first red arrow). Following conversion, the LWSS takes the path of the second red arrow, to become one pixel of a row. All of the memory loops work in the same way and are slightly displaced in height to produce LWSS in separate rows. | The gliders loop following the yellow arrows with the help of “Reflectors” placed at either ends. Additionally at the bottom end there is a glider duplicator. It produces a glider that moves parallel to the original. While the duplicated glider is sent back into the loop, the original glider is sent to a “Converter” which converts the glider to a LWSS (moves along the first red arrow). Following conversion, the LWSS takes the path of the second red arrow, to become one pixel of a row. All of the memory loops work in the same way and are slightly displaced in height to produce LWSS in separate rows. | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 1 May 2016
Game of Life and Universal Computation
Game of Life
Life, along with this “Game of Life”, is simply a mathematical model of a self-replicatable machine. It was named “Game of Life” since the rules of the game are similar to life of an organism although over-simplified.
“Game of Life” is played on a theoretically infinite, 2 dimensional square grid where each cell of the grid can take one of two states: “Alive” or “Dead”. The game requires the player to put in an initial pattern of living and dead cells and a program, following some rules, computes the next generation of the pattern. The standard rules of Life are:
- Any live cell with less than 2 live cells in the surrounding 8 cells will die (loneliness)
- Any live cell with more than 3 live cells in the surrounding 8 cells will also die (overcrowding)
- Any live cell with 2 or 3 live cells in the surrounding 8 cells will continue to live to the next generation
- Any dead cell with exactly three live cells in the surrounding 8 cells will come alive (reproduction)
A very good program for exploring cellular automata including “Game of Life” is “Golly”. Operating it is as simple as MS Paint, and it make things much easier to procure the numerous generations.
There are some basic patterns occurring frequently:
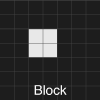
The patterns which remain still for all subsequent generations are called 'Still Lives'. Examples include the “Block” and the “Beehive”.
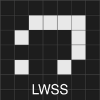
Some patterns moving across the field at different speeds and directions are called spaceships. The smallest spaceship is known as the “Glider”. The “LWSS” is short for “Light Weight Space Ship”.
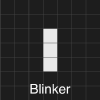
Other patterns repeat after certain generations while maintaining their positions. These are called oscillators. The “Blinker” and the “Beacon” are the most common oscillator.
Golly Ticker
The more complex patterns must be constructed from a set of basic patterns. The “Golly Ticker” is also no exception. Let’s see what it does first.
When you start generating it, you should see the word “Golly” (with a stylized “o”) move across the screen and then disappear at the left. This process continues infinitely, just looks like a stock ticker.
First, let's start with the Life objects that make up the text "Golly". The text is made up of what is known as the “Light Weight Space Ship” or LWSS for short. These Life objects continuously move in one of the four directions — up, down, left or right but never diagonally. Their speed is often expressed as a fraction of “c” or the speed of light. The speed of light taken in the context of Life refers to advancement of one cell per generation and this is the fastest a Life object can move.
The “Glider” (mentioned above) can move only diagonally at c/4 whereas the LWSS can move orthogonally at c/2. We can easily verify this using Golly, running slowly enough to clearly see the movements of each generation.
Each letter is 9 LWSSs in height, except for the "O" which is 11 LWSSs in height. If you take a close look at the characters, not all LWSSs are in the same phase. Some seem to "point" downwards and the rest upwards.
At the left end, there are structures called "Eaters" or “Fishhook". Just flanked one either side by them are the patterns known as "Kok's Galaxy".
Eaters are “Still Lives” which can eat away many objects without sustaining permanent damage. The job of the eater here is to assimilate the LWSSs coming in from the right. Since we have two distinct phases of LWSSs, the eater must be oriented properly to perform its job, otherwise the LWSSs will permanently destroy the eater. Kok's Galaxy belongs to the class of oscillators. Functionally, the generations of Kok's Galaxy flanking the eaters don't serve any purpose since deleting them doesn't affect the ticker at all.
The text is generated row by row. It starts by first creating the rows in the middle — the sixth and seventh rows. Rows 1 to 6 are created by the six structures at the right-top which are called “memory loops”. The other five are created by the five memory loops at the right bottom. The memory loops hold a specific pattern made of gliders that keep looping in the structure. At one end, they are duplicated where one glider is fed to the "Converter" and the other back into the memory loop.
The gliders loop following the yellow arrows with the help of “Reflectors” placed at either ends. Additionally at the bottom end there is a glider duplicator. It produces a glider that moves parallel to the original. While the duplicated glider is sent back into the loop, the original glider is sent to a “Converter” which converts the glider to a LWSS (moves along the first red arrow). Following conversion, the LWSS takes the path of the second red arrow, to become one pixel of a row. All of the memory loops work in the same way and are slightly displaced in height to produce LWSS in separate rows.