No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
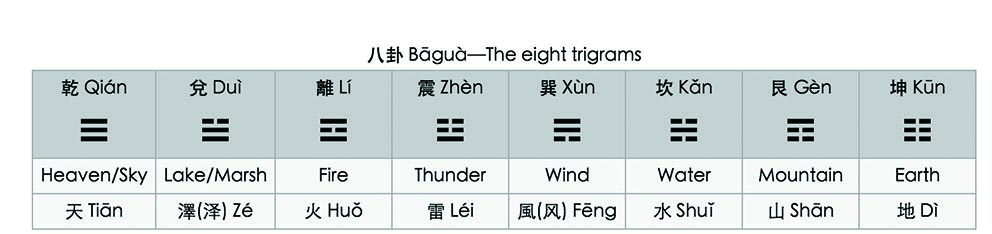
The bagua(eight trigrams )represents the fundamental principles of reality, seen as a range of eight interrelated concepts. Each consists of three lines, each line either "broken" or "unbroken," respectively representing yin or yang. The trigrams have correspondences in astronomy, astrology, geography, geomancy, anatomy, the family, and elsewhere. Bagua represents the early Chinese philosophy, it also has an impact on traditional Chinese medicine, martial arts, music and mathematics. | The bagua(eight trigrams )represents the fundamental principles of reality, seen as a range of eight interrelated concepts. Each consists of three lines, each line either "broken" or "unbroken," respectively representing yin or yang. The trigrams have correspondences in astronomy, astrology, geography, geomancy, anatomy, the family, and elsewhere. Bagua represents the early Chinese philosophy, it also has an impact on traditional Chinese medicine, martial arts, music and mathematics. | ||
[[File: | [[File:bagua3.jpg]] | ||
[[File: | [[File:bagua.jpg]] | ||
[[File:bagua1.jpg]] | |||
Revision as of 08:39, 2 June 2016
The bagua(eight trigrams )represents the fundamental principles of reality, seen as a range of eight interrelated concepts. Each consists of three lines, each line either "broken" or "unbroken," respectively representing yin or yang. The trigrams have correspondences in astronomy, astrology, geography, geomancy, anatomy, the family, and elsewhere. Bagua represents the early Chinese philosophy, it also has an impact on traditional Chinese medicine, martial arts, music and mathematics.