InterFace: How You See Me
InterFace is an interactive tool which uses the facial expressions to detect the emotions and creates an additional layer of communication between the viewer and the wearer. When an emotion is detected on the wearer side, it is translated into a set of colors to be seen by the viewer who is also triggered by the colors that has a relatively universal meaning.
Abstract
The evolutionary development of human resulted in many features to create greater societies from extensive groups of people, ideally living in harmony with each other. One of the most influential features that bring us the ability to build and sustain these social structures is our ability to empathize with the other people around us. However, in modern societies, we are getting more and more apart from each other and lost in the rush of our modern-day problems. Our perception of social interactions gets trapped in a closer circle even though we are encountering many different faces even in one day of our lives. As those faces got blurry for us, the lifting effect of being social and sharing decays even more. The project evaluates the effects of emotions through facial expressions in the contexts of empathy and modern-day social structures.
The process of empathy starts with people imagining themselves in another person’s shoes and trying to form meaning out of it. This involves paying attention to their body language, facial expressions, tone of voice, and words, as well as considering their past experiences and current circumstances. Several experts think that mirror neurons, or at least a similar mechanism, play a role in some forms of basic empathy. Mirror neurons in the mouth and the ability to imitate facial expressions are likely the foundation for being in tune with others emotionally. While the embodiment of emotions does not cover all aspects of empathetic experience, it provides a straightforward explanation of how we may share emotions with others and how this skill could have evolved through evolution (Coudé & Ferrari, 2018).
Moreover, it is a naturally evolved survival mechanism to avoid an unwanted situation with the help of others around. According to the findings of Adams et al(2006), two studies suggest that there is accuracy in detecting movements in angry and fearful faces, either moving towards or away from the observer. They found that observers were quicker to correctly identify angry faces moving towards them, suggesting that anger displays convey the intent to approach. However, the results were not the same for fear faces, which may indicate that fear signals a "freeze" response rather than a behavior of fleeing. Therefore, translating the emotions of one party to another has an essential role in sharing “data” collected from the outer world sensed by human body receptors. Besides the expressions of emotion being a means of non-verbal communication, unlike the gestures that can change from culture to culture, they are also relatively universal. According to Ekman(1970), basic emotions have a pancultural nature in that they are identified and also expressed in similar ways in different cultures with the same facial muscle responses.
While the embodiment of emotions through facial expressions it is a means of communication with the outer world. However, it’s the distinction between vocal communications etc. not being self-reflective that people cannot see or feel the immediate effect of their actions. Rather it is moving to the other party to be evaluated and has its effect on them and that is where the reflection forms. So one person feels the emotion but the other one sees the facial expression. The viewer is the bridge to the outer world as well as the reflection of the inside.
To explore the nature of these interactions through facial expressions of emotions in a bigger picture and to disrupt the woven structure of daily life, InterFace pursues to create a space for emphasizing the power of these individual emotions becoming visible and vivid for the outside world.
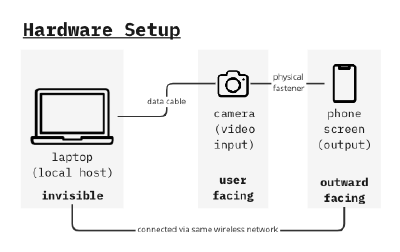
Hardware Setup
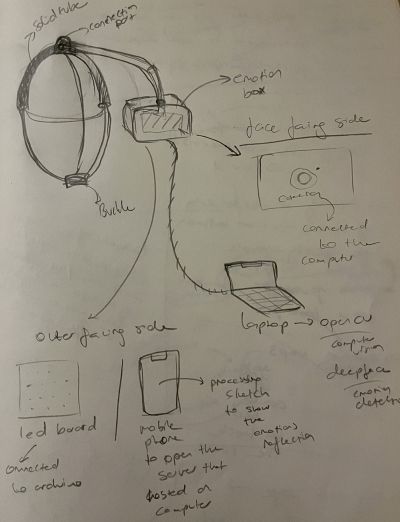
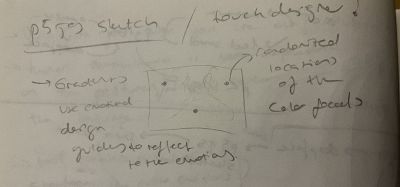
Initial Sketch
Experiments with the holder
Placed on head, camera facing the wearer, screen facing out.
Tools used;
- Phone holder
- Headphones
- Bİke Helmet
This model of display did not work, because the holder was too heavy to be balanced on the head. And since the camera cannot be too close to the face(to see and detect the face) the weight distribution was faulty.
Placed on the shoulder, camera facing the wearer, screen facing out.
- Phone holder
- Adjustable strap
File:Emotiondet 19.JPG //change this
This model was more stable than the head ones. The holder is clipped to the strap to ensure the stability with the help of the upper body that the strap goes around.
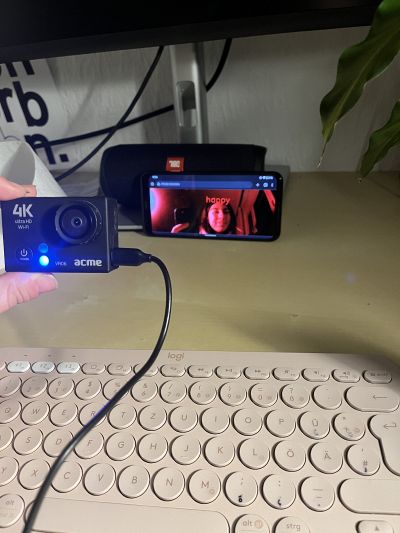
Camera
An external camera (an action camera which has a wide angle lens built-in) successfully set within the software setup process, which was more or less a cyclical process that went together with the hardware setup.
Hardware System Diagram
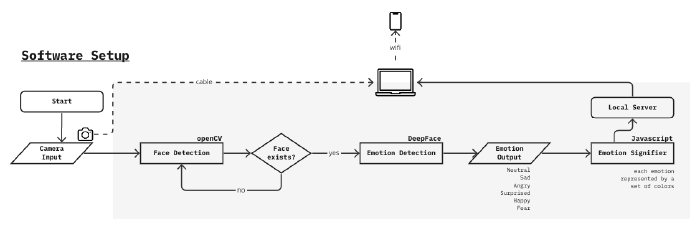
Software Setup
Phase 1: Backend
Sources used;
- OpenCV Face Detection
- DeepFace Emotion Recognition
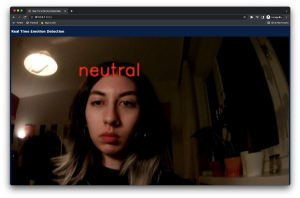
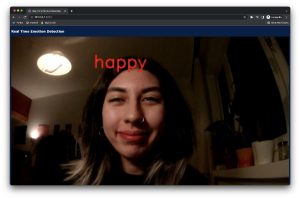
Starting with the OpenCV library which enabled face detection from the camera input, instances of the face each second are fed to DeepFace algorithm. DeepFace gives an output of the emotional data, labeled on the face.
The default emotion read-write was too fast(<1 sec intervals) to be used for a more stable visual which will be done in the further process, therefore a limiter is designed to output the emotion only when the same emotion is shown at least 2 times in a row.
Phase 2: Frontend
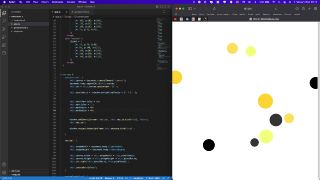
The emotion output is used for controlling a simple p5.js sketch on the website where all emotion detection visual coming together. This experiment was successful so it created space for elaborating the emotion driven visual.
Phase 3: Emotion Signifier Visual
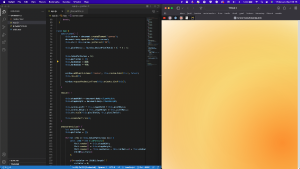
Using pure javascript, a particle system consisting of several ellipses in different sizes and with different alpha values in their color, moving gradient effect is created.
To select the colors signifying emotions, a research on color psychology is made to better understand the interpretation of colors. The psychological effects of colors on human mood and behavior stem from the electromagnetic radiation of light and are a universal, psychophysical response that is less impacted by factors such as culture, age, and gender than commonly believed. It's important to distinguish between color psychology and color symbolism. Color symbolism refers to the context in which colors are used, while the psychological properties of colors relate to the general moods they evoke in people(Wright, 2008 as cited in Kurt & Osueke, 2014). In the context of this project, the visual aims to transfer the general feeling to viewer rather than putting it inside the limits of an emotion by putting a layer to distort the reality.
Colors representing the wearer's emotions are
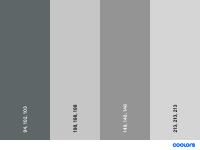
- Neutral
Colors from nature such as greens and earthy tones to trigger the calm feeling
- Sad
Gray tones to represent the "missing"
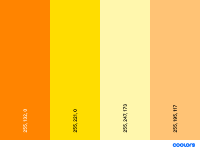
- Happy
Orange and yellows to which are connected to optimistic thoughts.
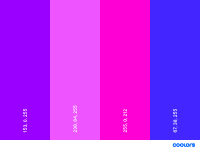
- Surprised
Bright purple and magenta to trigger the curiosity
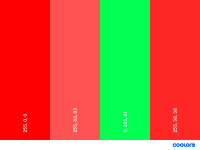
- Angry
Dark reds to trigger the negative/hostile feelings
- Fear
Bright red and green to trigger the alertness
Phase 4: Connection to the hardware & collecting the signifier output
For showing the same web page that is hosted on the laptop, the phone used as the screen should be connected to the same wifi. This method has its disadvantages and advantages such as not being able to make it full screen on the phone(not impossible but also not easy since the wearer has so little control over the screen) but also there is no significant latency for the display of the emotion signifier output.
An alternative to this solution might be broadcasting the laptop screen directly on a platform so that when it is displayed on the phone screen, the control is easier, while it requires a remote operator of the laptop. However after the experiments, using the tools OBS and YouTube streaming, there was a long latency period that the visual loses its purpose of being in sync with the real facial expression of the wearer. Therefore it is better to go with the first option which connecting via wifi.
Phase 5: Interactions
Video Walk
Discussions
- emotion detection with AI
- inclusivity, color blindness
References
Ekman, P. (1970). Universal Facial Expressions of Emotions. California Mental Health Research Digest, 8(4), 151-158.
Adams, R. B., Ambady, N., Macrae, C. N., & Kleck, R. E. (2006). Emotional expressions forecast approach-avoidance behavior. *Motivation and Emotion*, *30*(2), 177–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11031-006-9020-2
Ferrari, P. F., & Coudé, G. (2018). Mirror neurons, embodied emotions, and empathy. *Neuronal Correlates of Empathy*, 67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-805397-3.00006-1
DeepFace https://github.com/serengil/deepface
OpenCV https://opencv.org
early sensor experiments