[DRAFT]
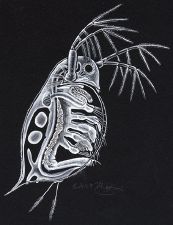
Daphnia pulex, although often called water fleas, are freshwater crustaceans closely related to shrimp. Daphnia, the most common microscopic crustacean, can be visible to the naked eye, with lengths ranging from 0.2–5 mm. Their reproduction alternates between asexual and sexual reproduction, with females laying eggs during the warmer season and males only being produced during stressed conditions, such as overcrowding or cold temperatures.
Daphnia are metazoan organisms, like nematodes, bristle worms, and tardigrades. Metazoa feeds on algae and bacteria, and algae- and bacteria-consuming protozoa like amoeba, flagellates, and ciliates. Protozoa control the bacterial population and pathogens, cycle nutrients, and improve water clarity. Metazoa keeps protozoa and bacterial populations in check.
1. Setting Up the Aquarium
A small aquarium was used to contain the daphnia.
For the water requirement, 1.5L Volvic brand mineral water was used to maintain the pH between 6.5 and 8.5. Since Daphnia are sensitive to chlorine, the water must be dechlorinated water.
The water plant and the snails were placed to regulate the oxygen inside the water and to filter.
Also, the water temperature must be between 18°C to 25°C, therefore, the tank was placed in the daylight in the lab to provide sufficient conditions.
2. Introducing the Culture
3x90 ml Daphnia culture was introduced to the tank.
3. Feeding the Daphnia
...
4. Maintaining Water Quality
...
5.Troubleshooting
...
Documentation by Melisa Aslan
References
Daphnia pulex. (n.d.-b). Retrieved on 06.09.2024 from https://cfb.unh.edu/cfbkey/html/Organisms/CCladocera/FDaphnidae/GDaphnia/Daphnia_pulex/daphniapulex.html
Hill, P. (2022, August 17). Lagoon Water fleas as indicator organisms: About Daphnia | Triplepoint Environmental. Triplepoint Environmental. Retrieved on 06.09.2024 from https://lagoons.com/blog/algae/lagoon-water-fleas/
Wikipedia. (2023, December 3). Daphnia pulex. Retrieved on 06.09.2024 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Daphnia_pulex






