HUMAN AND NONHUMAN PERFORMANCES TWO PROJECT
Hello
My name is Smin Kim. I'm studying Media art and design(M.F.A) at Bauhaus University Weimar.
Currently living and working in Weimar. Nice to see you here!
:)
Inspiration
Liquid Emulsion on stone

>>google search to Liquid Emulsion
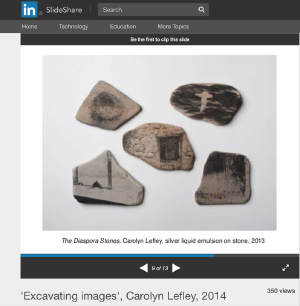
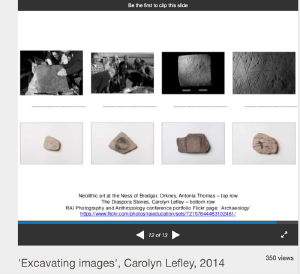
'Excavating images', Carolyn Lefley, 2014
Slides to illustrate a paper presented at the RAI Anthropology and Photography conference, British Museum. May 2014
http://www.slideshare.net/lefley/excavating-images-carolyn-lefley-2014
Liquid emulsion
=
With a liquid silver emulsion applications can be made to a variety of surfaces such as tile, glass, pottery, wood, canvas, stainless steel and coated metals. Brushing, dipping, and spraying are among the techniques employed for applying the emulsion to three-dimensional surfaces.
How to make it?
Alternative Photography - Printing Photos on Objects
http://www.instructables.com/id/The-Darkroom-Liquid-Light-Emulsion/
Another alternative way to use WAX
http://www.alternativephotography.com/wp/processes/liquid-emulsion/liquid-light-emulsion-on-wax
Books
Anthotypes – Explore the darkroom in your garden and make photographs using plants
http://www.alternativephotography.com/wp/processes/anthotypes/anthotypes
Lichen


A lichen is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria (or both) living among filaments of a fungus in a symbiotic relationship. The combined life form has properties that are very different from the properties of its component organisms. Lichens come in many colors, sizes, and forms. The properties are sometimes plant-like, but lichens are not plants. Lichens may have tiny, leafless branches (fruticose), flat leaf-like structures (foliose), flakes that lie on the surface like peeling paint (crustose),or other growth forms.
Lichens occur from sea level to high alpine elevations, in a very wide range of environmental conditions, and can grow on almost any surface.
Different kinds of lichens have adapted to survive in some of the most extreme environments on Earth: arctic tundra, hot dry deserts, rocky coasts, and toxic slag heaps. They can even live inside solid rock, growing between the grains. Some lichens do not grow on anything, living out their lives blowing about the environment. It is estimated that 6% of Earth's land surface is covered by lichen.
Symbiotic relation
A lichen is a composite organism that emerges from algae or cyanobacteria living among the filaments (hyphae) of a fungus in a mutually beneficial (symbiotic) relationship. The fungus benefits from the algae or cyanobacteria because they produce food by photosynthesis. The algae or cyanobacteria benefit by being protected from the environment by the filaments of the fungus, which also gather moisture and nutrients from the environment, and (usually) provide an anchor to it.
Evidence that lichens are examples of successful symbiosis is the fact that lichens can be found in almost every habitat and geographic area on the planet. Two species in two genera of green algae are found in over 35% of all lichens, but can only rarely be found living on their own outside of a lichen.
Growth rate
Lichens often have a regular but very slow growth rate of less than a millimeter per year. Different lichen species have been measured to grow as slowly as 0.5 mm, and as fast as 0.5 meter per year.
In crustose lichens, the area along the margin is where the most active growth is taking place. Most crustose lichens grow only 1–2 mm in diameter per year.
reports from Joe ̈l Boustie and Martin Grub
Lichens are characterized as a stable and self-supporting association between fungi—the mycobionts—and photo- autotrophic, algal partners—the photobionts.
About 18,500 different lichen species have been described all over the world. They may grow under rather diverse and sometimes extreme ecological conditions. Lichens can be found in very cold and dry
Lichen auf Stein
9.June // Blender Marker bought
10.June // Transfer image Experiments
1. Wood
2. Surface on wood
3. Flat stone
4. Making smooth flat stone
5. Curve stone

The Miller-Urey Experiment
What Was The Miller-Urey Experiment?
<videoflash type=YouTube>NNijmxsKGbc?list=PL75310AD28DB37A33</videoflash> Made by Stated Clearly http://statedclearly.com/
The Miller-Urey experiment was the first attempt to scientifically explore ideas about the origin of life. Stanley Miller simulated conditions thought be common on the ancient Earth. The purpose was to test the idea that the complex molecules of life (in this case, amino acids) could have arisen on our young planet through simple, natural chemical reactions.
The idea was to simulate hypothetical conditions thought to be present on the early Earth (Hadean or early Archaean). It was a test of the chemical origins of life. Specifically, the experiment tested Alexander Oparin's and J.B.S. Haldane's hypothesis that conditions on the primitive Earth favored chemical reactions that synthesized organic compounds from inorganic precursors. Considered to be the classic experiment on the origin of life, it was conducted in 1952 and published in 1953 by Stanley Miller and Harold Urey at the University of Chicago.
After Miller's death in 2007, scientists examined sealed vials preserved from the original experiments. They were able to show that there were well over 20 different amino acids produced in Miller's original experiments. That is considerably more than those Miller originally reported, and more than the 20 that naturally occur in life.
source from https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Miller%E2%80%93Urey
Die Antwort vom Fachchemiker
Zu Punkt 3 muss ich recht unverschämt und auch unhöflich zurück fragen: was haben Sie als Studentin für eine Ausbildung ? Bio oder Bioart ist was anderes als chemische Experimente, noch dazu mit potentiell gefährlichen Substanzen. ich gehe davon aus, dass das erst mal nicht bei Dir daheim stattfinden soll - davon muss ich massiv und entschieden abraten !!! hat die Bauhaus Uni überhaupt irgendwelche chemische Labors ?? nochmals: Bio und Bioart haben NICHTS mit chemischen Experimenten zu tun !! "sicher" kann man das Experiment nur machen, wenn fachkundige Leute damit am Werk sind und die die passenden Labors und Apparaturen dazu haben grundsätzlich hand habt man hier entweder hochgiftige, korrosive oder potentiell explosive Ausgangssubstanzen (mit Kohlenmonoxid kann man Lebewesen umbringen) wenn man das Experiment wirklich hinbekommt, muss die entstandene "Suppe" auch noch analysiert werden, dazu braucht es Maschinen und Menschen die das können. meine persönliche Meinung ist noch: wenn man das Experiment wiederholt und gefahrlos übersteht, ist die Suppe auf jeden Fall anders zusammen gesetzt generell würde ich nur abraten davon, andere haben das schon gemacht und außer Gefahr beim Umgang damit kommt nichts raus, was gewinnbringend ist; organische Produkte sind möglicherweise ein Ausgangspunkt aber noch kein Leben. Ich finde, dass man mit Bioart schönere Sachen machen kann. Entschuldigung wenn es etwas heftig war, entspricht aber der Reaktion in dem 'geplanten' Reaktor.
I would get advice from Korean students of the Faculty of Biology and Pharmacy, Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena.
Cut_layer
Karl Bloss Feldt
Urformen der Kunst, 1928
Goethe
Metamorphosis of Plants, 1786
Maria Sibylla Merian
Der Raupen wunderbarer Verwandlung, 1679
Royal Horcticultural Society des Blumen büros Hollands
Bloemen bureau Holland,
Pantone-System
