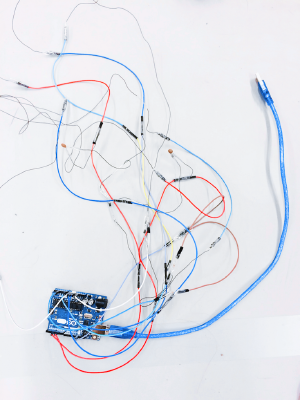
Introduction
This is a tutorial about how to control Arduino by Captury. A vibration motor will be used in Arduino as a trigger. So it’s mainly about how to control the motor by using the received data of Captury. In Arduino, there is also a small tutorial about how to trigger the vibration motor by using the photocell sensor, which is related to my project module, Wool's World.
Basically, the tutorial is divided into two parts. The first part is about the basic steps to control the vibration motor by using the photocell sensor. And for the second part which I will show you how to control it by Captury.
First Part
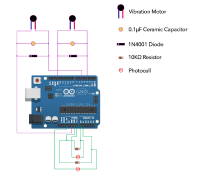
In this part I will show you how to use two photocells to control the on/off of two vibration motors in Arduino. The trigger was designed as if two photocells are covered by hands, then those vibration motors will vibrate simultaneously.
Hardware You Need: (for each item x2)
Photocell
Vibration Motor
Arduino Board
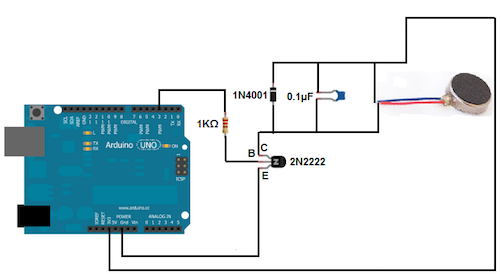
1N4001 Diode
0.1µF ceramic capacitor
10KΩ Resistor
2N2222 NPN Transistor
USB Connector
So how do I test if the vibration motor works well?
The following circuit is the basic method to test your motor without photocell:
TIPS! For this circuit you may need a 1KΩ Resistor.
The Code for Test:
(The code vibrates the motor every minute)
const int motorPin = 3;
void setup()
{
pinMode(motorPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(motorPin, HIGH);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(motorPin, LOW);
delay(59000);
}
After test successfully, you can build a circuit with photocell as a following diagram:
The Code Using Photocell:
int photocellPin = 0; // the cell and 10K pulldown are connected to A0
int photocellPin1 = 1; // the cell and 10K pulldown are connected to A1
int photocellReading, photocellReading1; // the analog reading from the sensor divider
void setup() { // We'll send debugging information via the Serial monitor
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(5, OUTPUT);
}
void loop(void) {
photocellReading = analogRead(photocellPin);
photocellReading1 = analogRead(photocellPin1);
if(photocellReading < 400 && photocellReading1 < 400 ){
digitalWrite(3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(5, HIGH);
delay(100);
}
else {
digitalWrite(3, LOW);
digitalWrite(5, LOW);
delay(100);
}
Serial.print("Analog reading1 = ");
Serial.println(photocellReading); // the raw analog reading1
Serial.print("Analog reading2 = ");
Serial.println(photocellReading1); // the raw analog reading2
Serial.println(" ");
delay(10);
}TIPS! Considering different light intensity in different environment, you may have to change the value of 'photocellReading' (Line15) if it's not work.
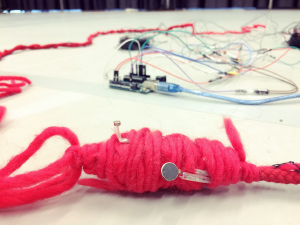
For a better experience, I built two handles with red wools and extended the length of the circuit.
Test Video
Second Part
To control an Arduino with the Captury, you have to use OSC(Open Sound Control) as a bridge. In this case, I would like to use the data of tracking system to control my vibration motor.
Before writing your code in Arduino, make sure that you have installed the library about OSC you need. Here I used theOSC library written from University of Berkeley.
Basically, the code below has the function of receiving data from Captury via OSC, and the speed data of the tracked person's movement will control the value of photocell sensor, which will trigger the vibration motor at the same time.
The Code Controlling with Captury:
#include <OSCMessage.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
#include <EthernetUdp.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <OSCBoards.h>
#include <OSCBundle.h>
EthernetUDP Udp;
byte mac[] = {
0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED }; // you can find this written on the board of some Arduino Ethernets or shields
//the Arduino's IP
IPAddress ip(128, 32, 122, 252);
//destination IP
IPAddress outIp(128, 32, 122, 125);
OSCMessage msg;
//SLIPEncodedSerial SLIPSerial;
//port numbers
const unsigned int inPort = 1065;
const unsigned int outPort = 1065;
int photocellPin = 0; // the cell and 10K pulldown are connected to a0
int photocellReading; // the analog reading from the sensor divider
int x1=0; int y1=0; int z1=0; int x2=0; int y2=0; int z2=0;
int temptime,time1,time2;
float vel;
void setup() {
// We'll send debugging information via the Serial monitor
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(3, OUTPUT);
//setup ethernet part
Ethernet.begin(mac,ip);
Udp.begin(inPort);
//Recording the original position and running time
x1 = msg.getFloat(0);
z1 = msg.getFloat(1);
y1 = msg.getFloat(2);
time1 = millis();
}
void OscMsg(OSCMessage &msg){
OSCBundle bundleIN;
int size;
if( (size = Udp.parsePacket())>0)
{
while(size--)
bundleIN.fill(Udp.read());
if(!bundleIN.hasError())
//OSCMessages can be routed to a specific function(GetPosition) by matching their address partial
bundleIN.route("/blender/Root/vector",GetPosition);
}
}
void GetPosition(OSCMessage &msg){
//Recording the distance between two points
float x = msg.getFloat(0);
float z = msg.getFloat(1);
float y = msg.getFloat(2);
x2 = abs(x - x1);
y2 = abs(y - y1);
x2 = abs(z - z1);
x1 = x;
y1 = y;
z1 = z;
float distance = sqrt(sq(x2)+sq(y2)+sq(z2));
//Record the duration time that this bone move from the first point to the second point
temptime = millis();
time2 = (temptime - time1)/1000;
//Calculate the velocity of this bone
vel = (distance/time2)*100;
}
void loop(void) {
//photocellReading = analogRead(photocellPin);
//Giving the velocity to 马达
OscMsg(msg);
photocellReading = vel;
if(photocellReading < 600){
digitalWrite(3, HIGH);
delay(100);
}
else if(photocellReading > 600){
digitalWrite(3, LOW);
delay(100);
}
Serial.print("Analog reading = ");
Serial.println(photocellReading); // the raw analog reading
delay(10);
}TIPS! Also, you have to make sure that you used the right port related with the Captury.