No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Evolution and Endosymbiosis= | ==Evolution and Endosymbiosis== | ||
"Endosymbiotic theory, that attempts to explain the origins of eukaryotic cell organelles such as mitochondria in animals and fungi and chloroplasts in plants was greatly advanced by the seminal work of biologist Lynn Margulis in the 1960s." [http://www.fossilmuseum.net/Evolution/Endosymbiosis.htm] | |||
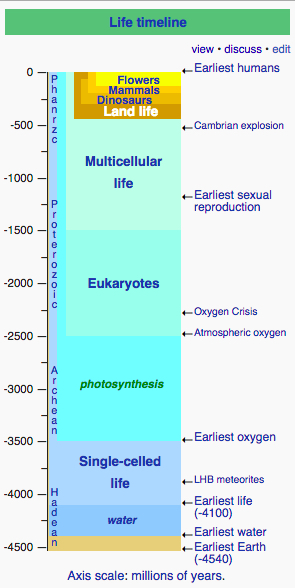
==Life timeline== | ==Life timeline== | ||
[[File:life-timeline.jpg|300px]] | [[File:life-timeline.jpg|300px]] | ||
| Line 32: | Line 34: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
*William B. Whitman (2009). "The Modern Concept of the Procaryote." JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 2009, p. 2000–2005 | *William B. Whitman (2009). "The Modern Concept of the Procaryote." JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 2009, p. 2000–2005 | ||
*fossilmuseum (2018). Endosymbiosis - The Appearance of the Eukaryotes, Available at http://www.fossilmuseum.net/Evolution/Endosymbiosis.htm | |||
Latest revision as of 19:30, 11 April 2018
Evolution and Endosymbiosis
"Endosymbiotic theory, that attempts to explain the origins of eukaryotic cell organelles such as mitochondria in animals and fungi and chloroplasts in plants was greatly advanced by the seminal work of biologist Lynn Margulis in the 1960s." [5]
Life timeline
Kingdom
- Animalia
- Plantae
- Fungi
- Protista
- Archaea
- Bacteria
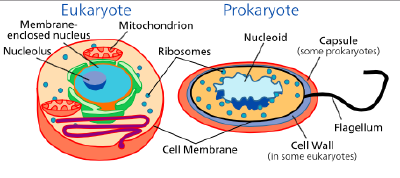
Prokaryotes and Eucaryotes
Phylogenetic tree
"A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities—their phylogeny—based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics." (Wikipedia, Phylogenetic tree)
Organisms
References
- William B. Whitman (2009). "The Modern Concept of the Procaryote." JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 2009, p. 2000–2005
- fossilmuseum (2018). Endosymbiosis - The Appearance of the Eukaryotes, Available at http://www.fossilmuseum.net/Evolution/Endosymbiosis.htm
![Phylogenetic tree [1]](/kunst-und-gestaltung/wiki/images/thumb/2000px-Tree_of_life_SVG.svg.png/120px-2000px-Tree_of_life_SVG.svg.png)

![Phylogenetic tree based on plastid [2]](/kunst-und-gestaltung/wiki/images/thumb/Screen_Shot_2018-04-11_at_11.11.20_AM.png/91px-Screen_Shot_2018-04-11_at_11.11.20_AM.png)
![Euglena Gracilis [3]](/kunst-und-gestaltung/wiki/images/thumb/Euglena_wikimedia.org.jpg/120px-Euglena_wikimedia.org.jpg)
![Drosophila Melanogaster [4]](/kunst-und-gestaltung/wiki/images/thumb/Drosophila_melanogaster_Proboscis-wikimedia.jpg/120px-Drosophila_melanogaster_Proboscis-wikimedia.jpg)